Resources
- What is Skipping School or Academic Neglect
- Skipping school or academic neglect can manifest in various ways
- Skipping school or academic neglect can have serious consequences
- Parents play a crucial role in addressing and preventing skipping school or academic neglect in their children.
- Statistics and Data
What is Skipping School or Academic Neglect
Skipping school or academic neglect refers to the act of deliberately avoiding attending school or neglecting one’s academic responsibilities. It is a form of truancy where a student misses school without a valid reason or repeatedly neglects their studies, leading to a decline in their academic performance and overall educational well-being.

Skipping school or academic neglect can manifest in various ways
Skipping school or academic neglect can manifest in various ways:


Truancy: Students may skip school without the knowledge or permission of their parents or school authorities. They may do this to avoid classes, tests, or assignments.

Chronic Absenteeism: Some students may develop a pattern of frequently missing school, leading to chronic absenteeism. This can have a significant negative impact on their academic progress and social development.

Lack of Interest: Academic neglect can result from a lack of interest in school and learning. Students may become disengaged from their studies and lose motivation to attend classes regularly.

Peer Influence: In some cases, students may skip school due to peer pressure or the influence of friends who encourage such behavior.

Academic Struggles: Students facing academic challenges or learning difficulties may skip school as a coping mechanism to avoid the stress and anxiety associated with poor performance.

Personal Issues: Academic neglect can also be a symptom of underlying personal issues such as bullying, mental health concerns, or problems at home.
Skipping school or academic neglect can have serious consequences
Skipping school or academic neglect can have serious consequences, including:
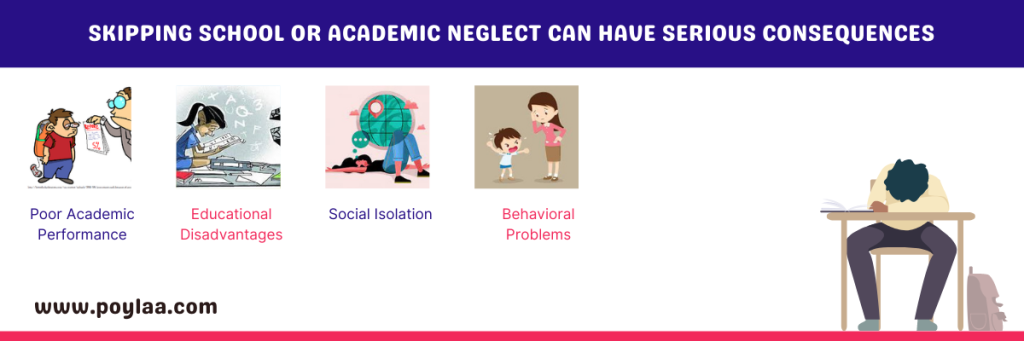

Poor Academic Performance: Regularly missing classes and neglecting studies can lead to falling behind in coursework and lower grades.

Educational Disadvantages: Academic neglect can hinder a student’s overall educational progress and limit their opportunities for future success.

Social Isolation: Chronic absenteeism can lead to social isolation as students miss out on building friendships and participating in school activities.

Behavioral Problems: Academic neglect may be associated with behavioral issues, as students may engage in other risky behaviors when not attending school.
To address skipping school or academic neglect, it is essential for parents, teachers, and school administrators to work together to identify the root causes and provide appropriate support and intervention. This may involve counseling, academic assistance, and creating a positive and supportive learning environment to re-engage the student in their studies and school life.
Parents play a crucial role in addressing and preventing skipping school or academic neglect in their children.
Parents play a crucial role in addressing and preventing skipping school or academic neglect in their children. Here are some strategies that parents can adopt to stop this behavior and promote regular attendance and academic engagement:
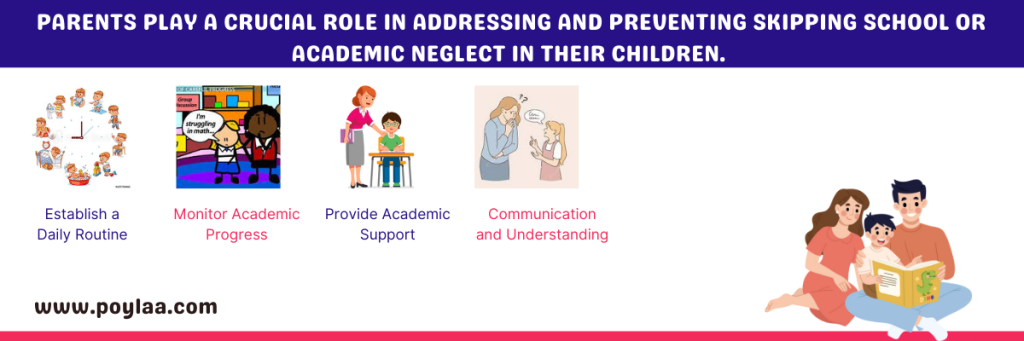

Establish a Daily Routine: Create a structured daily routine that includes specific times for waking up, meals, studying, and leisure activities. A consistent routine can help inculcate good habits and time management skills.

Monitor Academic Progress: Regularly monitor your child’s academic progress and stay informed about their school activities. Attend parent-teacher meetings and maintain communication with their teachers to address any concerns promptly.

Provide Academic Support: If your child is struggling academically, consider providing additional support, such as hiring a tutor or seeking help from the school’s counseling services.
Communication and Understanding: Open and non-judgmental communication is essential. Talk to your child about their feelings and experiences related to school. Understand if there are any underlying issues contributing to their absenteeism or academic neglect.
Statistics and Data
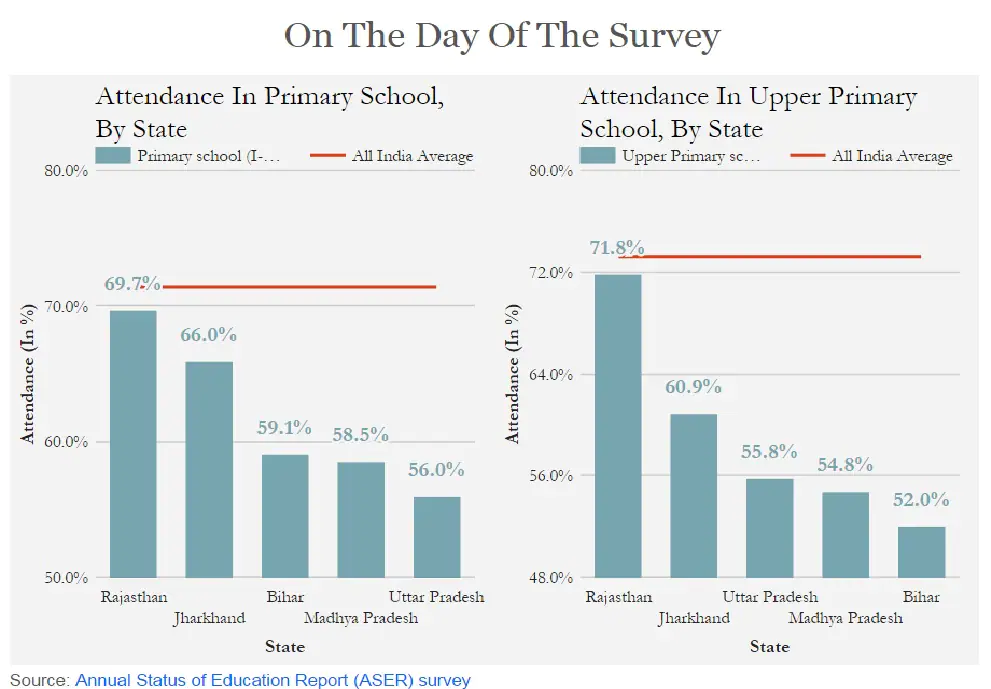
| Age Group | Dropout Rate (%) | Absenteeism Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 11 – 14 years | 3.5 | Not Available |
| 15 – 16 years | 13.5 | Not Available |
| Grades I – VIII | Not Available | 25.0 |
Note : i am using this dataset from https://www.firstpost.com/india/indias-great-education-challenge-low-attendance-high-rate-of-dropouts-plague-rural-schools-3378802.html