What is Unsafe Sexual Practices
Unsafe sexual practices among teenagers refer to behaviors that increase the risk of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and unintended pregnancies. These practices involve engaging in sexual activities without proper protection or taking necessary precautions.

Examples of Unsafe Sexual Practices
Some examples of unsafe sexual practices among teenagers include:

Unprotected Sex: Engaging in sexual intercourse without using condoms or other forms of barrier protection, which can lead to the transmission of STIs and increase the risk of unintended pregnancies.
Lack of Birth Control: Not using any form of birth control or contraception during sexual activity, which can result in unplanned pregnancies.

Multiple Sexual Partners: Having multiple sexual partners without using protection can increase the risk of exposure to STIs.

Alcohol and Drug Use: Engaging in sexual activity under the influence of alcohol or drugs, which may impair judgment and lead to risky sexual behaviors.

Lack of Communication: Failing to communicate openly with sexual partners about past sexual history, STI testing, and contraception can lead to misunderstandings and increase the risk of infection.

Lack of STI Testing: Not getting tested for sexually transmitted infections regularly, which can delay diagnosis and treatment.

Non-Consensual or Unwanted Sex: Engaging in sexual activity without consent or engaging in unwanted sexual activities, which can have severe emotional and physical consequences.
Stopping unsafe sexual practices among teenagers
Stopping reckless driving requires a collaborative effort between the Indian government and the police force. Together, they can implement effective strategies to promote road safety and discourage dangerous driving behaviors. Here are some key steps that can be taken:


Comprehensive Sexual Education: Implement comprehensive and age-appropriate sexual education programs in schools. These programs should cover topics like safe sex practices, STIs, contraception, consent, and healthy relationships.

Access to Reproductive Health Services: Ensure teenagers have access to confidential and youth-friendly reproductive health services, including STI testing, contraceptive options, and counseling.

Promote Consent Education: Teach the importance of consent and respect in all relationships, emphasizing that all sexual activities must be consensual.

Peer Education: Engage teenagers in peer-led education programs where they can discuss sexual health topics, share experiences, and support each other in making responsible choices.

Media Literacy: Teach teenagers to critically analyze media portrayals of relationships and sex to distinguish between reality and fiction.

Online Safety: Educate teenagers about the risks of engaging in unsafe sexual practices online, such as sharing explicit content or interacting with strangers, and how to protect themselves.

Address Gender Norms: Challenge harmful gender norms and stereotypes that may contribute to unsafe sexual practices and promote gender equality and respect.
Statistics and Data
| Age at Beginning of Full Sexual Relations | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|
| 16-20 years | 47% |
| 21-24 years | 53% |
| Contraception Usage | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|
| Protection (Most commonly used method) | 68% |
| Non-usage of Protection | 68% |
| Did not discuss contraception with partner | 65% |
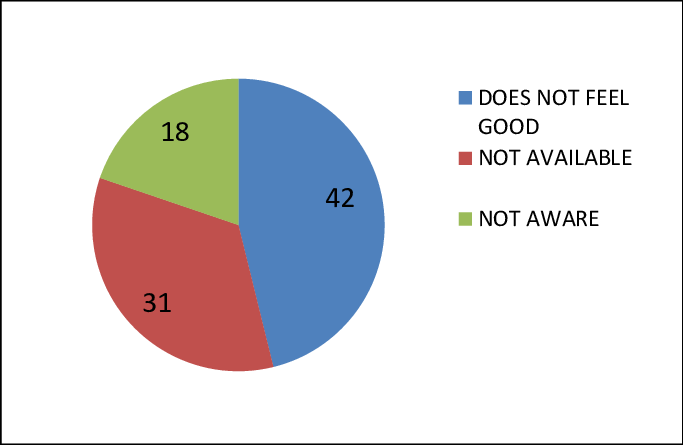
| Reasons for Not Using Contraception | Percentage of Participants |
|---|---|
| It does not feel good | 42% |
| Contraception not available at the time | 31% |
| Unaware of contraception | 18% |